Receding gums are a dental condition in which gums pull away from the teeth to expose tooth roots—leaving teeth vulnerable to decay and sensitivity to hot and cold. Receding gums can also result in a toothy smile that affects your confidence and well-being.
Several dental treatments are available to improve receding gums, and to prevent tooth loss and the progression of tooth decay. Here are common symptoms and causes of receding gums, and how to fix receding gums so you can improve your oral health and gain a more attractive smile.
Table of Contents
- Symptoms of receding gums
- Causes of receding gums
- Treatments for receding gums
- FAQs about receding gums
Symptoms of Receding Gums
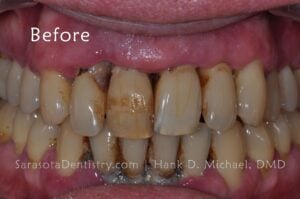
Receding gums are usually caused by gum disease and are frequently accompanied by other symptoms:
- Red or purple gums
- Swollen gums
- Tender gums
- Bleeding gums
- Bad breath
- Pain when chewing
- Plaque and tartar buildup
Causes of Receding Gums
Gum disease is the most common cause of receding gums, occurring when gum tissue becomes infected. Three out of four adults have some form of gum disease characterized by receding gums and other symptoms, reports the California Dental Association. Smoking, poor oral hygiene, and plaque and tartar buildup may cause gum disease.
Here are other causes of receding gums:
- Genetics and family history
- Hormonal changes and imbalances
- Certain medical conditions such as AIDS and diabetes
- Medications that cause dry mouth
- Brushing too hard
- Bruxism (grinding teeth)
- Crooked teeth
- Misaligned bite
- Poorly fitting dentures
A dentist can usually diagnose gum disease using a tiny ruler called a probe that measures pockets around the teeth. According to the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research, the pocket depth around teeth in a healthy mouth should measure between 1 and 3 millimeters. Pocket depth measurements above 3 millimeters may indicate the presence of gum disease.
Treatments for Receding Gums
Seeking treatment for receding gums as soon as possible can help prevent the progression of tooth decay, gum disease, and tooth loss. Your dentist may have options available for treating receding gums, including routine deep dental cleanings, scaling and root planing, and gingivectomy.
Scaling and Root Planing
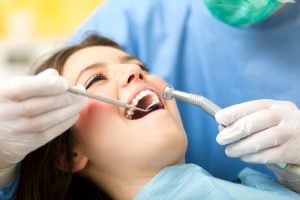
Scaling and root planing is a gum disease treatment that helps gums reattach to teeth. During this two-part procedure, your dentist removes plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline, including inside the pockets surrounding teeth. Then, your dentist smooths out tooth roots to promote gum reattachment. Results from a study published in the Journal of the American Dental Association show that scaling and root planing is a highly effective treatment for patients who have receding gums related to chronic gum disease.
Routine Deep Dental Cleanings
A deep dental cleaning is also known as scaling and root planing. If you have been diagnosed with gum disease, your dentist may have you come in for routine deep dental cleanings to maintain healthy teeth and gums—especially if your gum disease is chronic or advanced.
Soft Tissue Grafting
Soft tissue grafting helps promote the growth of new gum tissue to replace tissue that is lost or has receded due to plaque buildup. Soft tissue grafting uses gum tissue taken from your own palate or a donor’s, and is used to cover exposed tooth roots. This treatment for receding gums can improve the appearance of your smile and reduce the risk of tooth decay and sensitivity.
Gingivectomy
A gingivectomy is the surgical removal of gum tissue. This may be performed on gum tissue that is diseased or infected, or that may be loose and contributing to tooth loss. A gingivectomy can also help stop the progression of gum disease.
FAQs about Receding Gums
How can I tell if my gums are receding?
The most common signs of receding gums are teeth that look longer, teeth that are loose, and exposed tooth roots. Teeth may also be crooked or out of alignment due to loosened gum pockets.
Can receding gums grow back?
Receding gums cannot grow back on their own. However, dental treatments such as scaling and root planing, soft tissue grafting, and gingivectomy can all help promote the regrowth and/or reattachment of gum tissue.
Can I stop receding gums naturally?
Receding gums may be stopped or improved by practicing good oral hygiene, quitting smoking, and eating nutritious foods that promote strong, healthy teeth and gums. Some natural remedies for receding gums include peppermint, thyme, eucalyptus, and tea tree essential oils; turmeric; oil pulling; and green tea. However, these treatments may not fully repair or reverse the effects of gum disease and receding gums.
How can I stop receding gums from getting worse?
Your dentist can provide you with tips on how to prevent receding gums from becoming worse based on your unique oral health condition. Routine deep dental cleanings, daily brushing and flossing, and quitting smoking are some steps you can take to halt the progression of receding gums.
What treatments are available for receding gums?
Your dentist can consult with you on how to fix receding gums based on the progression of your gum disease or oral health condition. Scaling and root planing, soft tissue grafting, and gingivectomy are all effective treatments for receding gums.
Sarasota Dentistry offers several treatments for receding gums and gum disease that can help you achieve a healthier mouth and more attractive smile. Contact our office today at 941-929-7645 to schedule an appointment and learn more about your available treatment options.
- Dental Implant Pros and Cons - August 26, 2023
- Receding Gums Stages - August 12, 2023
- When Is It Too Late for Gum Grafting? - July 8, 2023


