Gum recession is a common dental problem. Fortunately, there are many ways to treat and sometimes reverse it. A dentist often recommends gum grafting when gum recession is in the advanced stages. Although effective, grafting may not work if delayed for too long.
We explore gum grafting and how it can restore a patient’s oral health. We also discuss the timing of gum grafting and when other procedures are more effective in treating advanced gum recession.
What Is Gum Grafting and When Would I Need It?
Gum grafting is a technique that covers exposed tooth roots and surfaces and revives existing gum tissue. Most dentists or periodontists perform three types of gum grafting. One is a sub-epithelial connective-tissue graft, which uses a piece of tissue below the surface of the skin located on the roof of the mouth. Free-gingival grafts utilize the outermost layer of the mouth roof, and pedicle grafts utilize the gum tissue next to the receding area.
Gum grafting typically occurs with local anesthesia and takes less than an hour. The procedure is relatively painless, and patients need little time to recover. Patients with more severe gun recession may need more than one appointment.
Gum grafting is a treatment for many cases of gum recession, when the gum tissue gradually moves away from the tooth, exposing more of the root and other surfaces. The most common culprit of gum recession is poor oral hygiene resulting in periodontal disease. Other contributors to receding gums include:
- Grinding teeth (awake or asleep)
- Injury to the gums
- Excessive toothbrushing (stiff brush or heavy hand)
- Misalignment in one’s bite
- Medication induced recession
- Malnutrition
- Eating disorders (i.e. anorexia or bulimia)
- Smoking
- Chewing tabacco
- Genetic predisposition (family trait)
Gum recession is more than just an aesthetic problem. Left untreated, it can leave a person more vulnerable to cavities, tooth sensitivity, decay, and even tooth loss. If a thorough professional cleaning does not solve the problem, it may be time to consider gum grafting.
When Is It Too Late for Gum Grafting?
When does gum grafting work for gum recession? If your dentist recommends gum grafting, it is essential to have the procedure done as soon as possible. Doing so will likely prevent further recession and help you avoid more serious oral health issues later.
Given your circumstances and oral health, your dentist may be able to determine at what point gum grafting would be successful, for example, if your gums show minimal damage or bone loss. If the damage to your gums is too extensive, the procedure may not solve your problem, or the odds of successful gingival graft may be diminished.
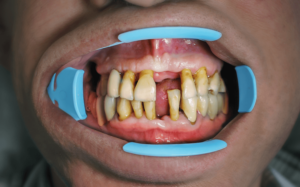
If your gum recession is advanced and you proceed with grafting, there is a slight chance of complications, such as pain, swelling, infection, and/or failure to heal properly resulting in a failed graft. Failures or complications are rare if an experienced surgeon is performing the procedure and you are a healthy candidate for gum grafting. It’s also very important to follow all post-op and pre-op instructions to get the best results from your gum grafting procedure.
If you do experience a gum graft may failure, it may be indicated by a section of white tissue that becomes separated. This signifies that the grafted section is no longer getting enough blood and is dying. You might also experience a fever of over 101 degrees Fahrenheit or see pus at the surgical site.
Contact your dentist or periodontist immediately for emergency care for any complications or symptoms of gum graft failure.
Is Gum Grafting the Right Option for Me?
Your dentist or periodontist can help you decide if gum grafting can restore your gums and teeth. During an initial exam, they will assess the amount of your gum recession and consider the underlying causes to determine if a gum graft is the appropriate course of action.
Before the procedure, your dentist will review all the steps with you and answer your questions. Be sure to ask about what you will require for aftercare and the follow-up appointment about a week after the graft.
During recovery, stick with cold and soft foods like soft- or hard-boiled eggs, yogurt, cottage cheese, gelatin, and soft-cooked vegetables. Healing should occur in one or two weeks, after which you can resume regular brushing and flossing. However, the grafted tissue may take about a month to heal completely.
- Dental Implant Pros and Cons - August 26, 2023
- Receding Gums Stages - August 12, 2023
- When Is It Too Late for Gum Grafting? - July 8, 2023


